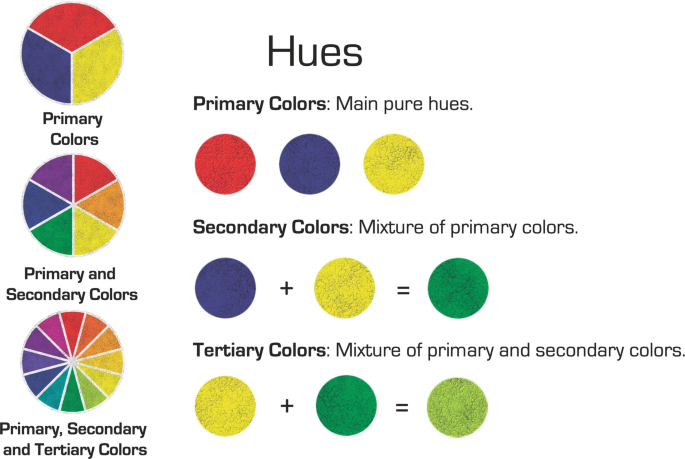
Colour - Wavelengths, Pigments, Light
Colour - Wavelengths, Pigments, Light: According to the law of energy conservation, energy can be converted from one form to another, but it cannot be created or destroyed. Consequently, when a photon of light is absorbed by matter, usually by an atom, molecule, or ion or by a small grouping of such units, the photon disappears and its energy is gained by the matter. Similarly, when matter emits light, it loses the energy carried away by the photons. A given atom or molecule cannot emit light of any arbitrary energy, since quantum theory explains that only certain energy states are possible for a given system.
Color, the aspect of any object that may be described in terms of hue, lightness, and saturation. In physics, color is associated specifically with electromagnetic radiation of a certain range of wavelengths visible to the human eye. Learn more about color in this article.
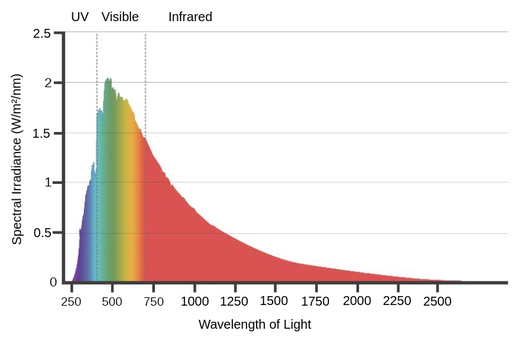
Pigment absorption spectra - Labster
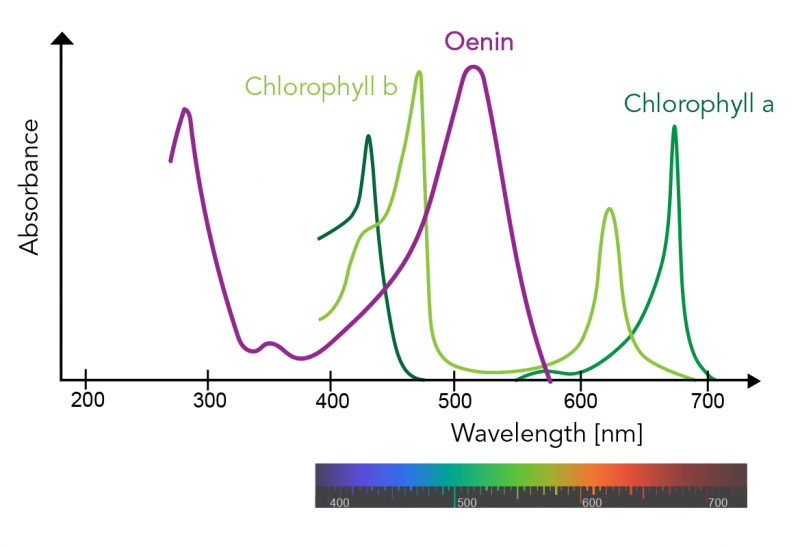
Plant Pigments Let's Talk Science
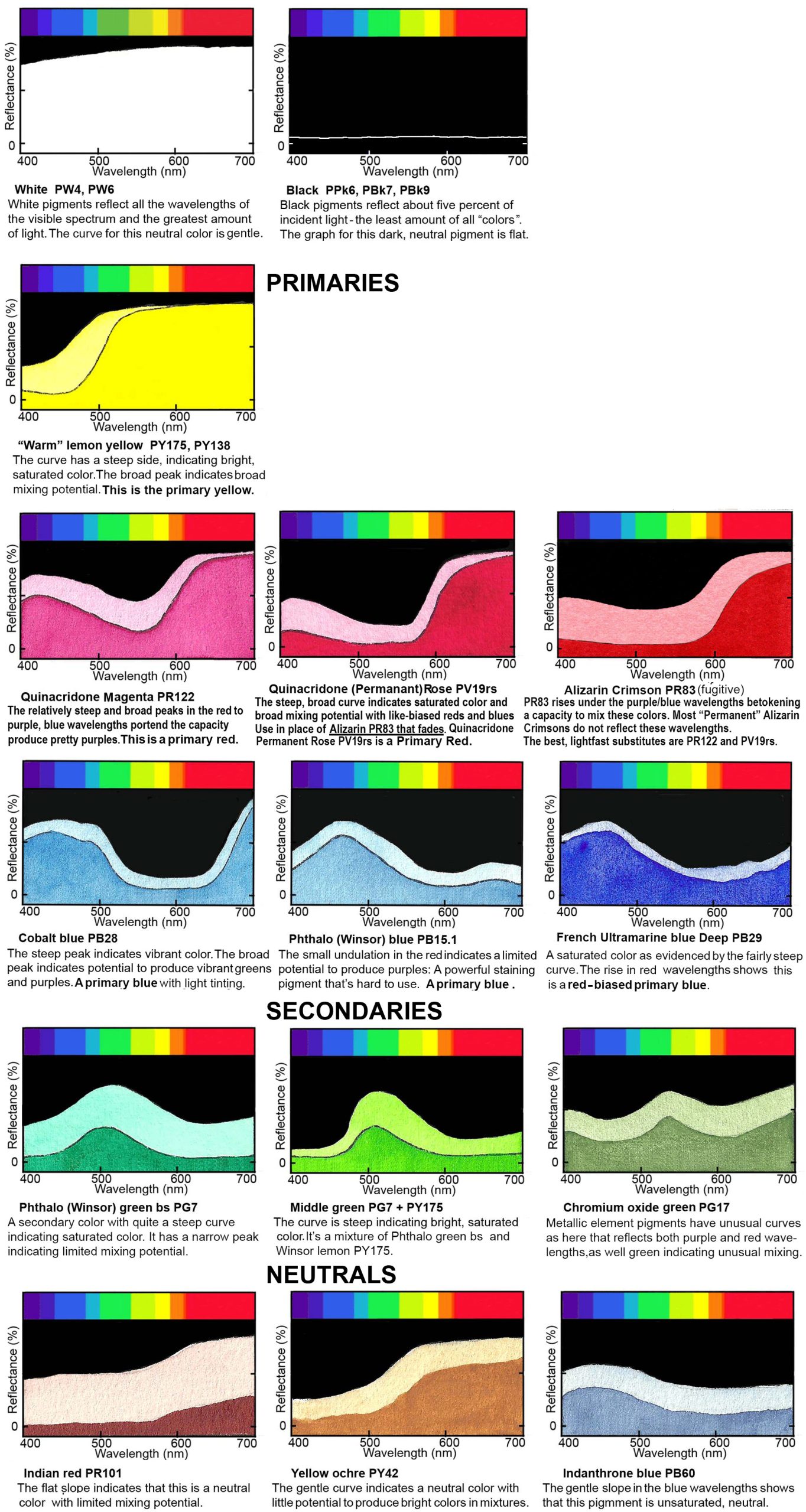
Reflectance Curves and Color
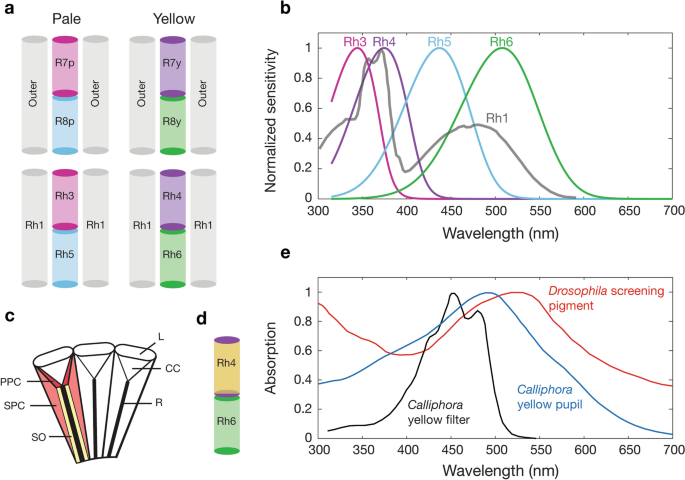
The spectral sensitivity of Drosophila photoreceptors
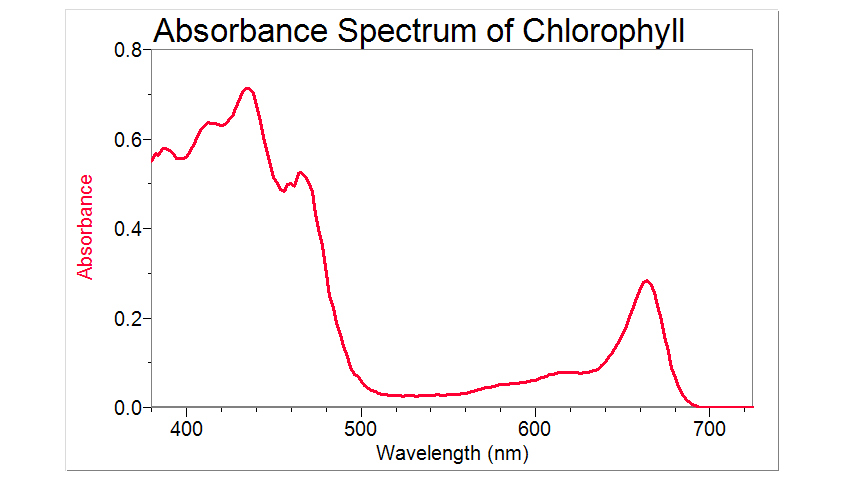
Plant Pigments > Experiment 14 from Investigating Biology through Inquiry
Which colour light is the best for photosynthesis between violet, blue, green, yellow, and red? - Quora
Spectrums of Light Biology for Majors I

optics - How does light combine to make new colours? - Physics Stack Exchange
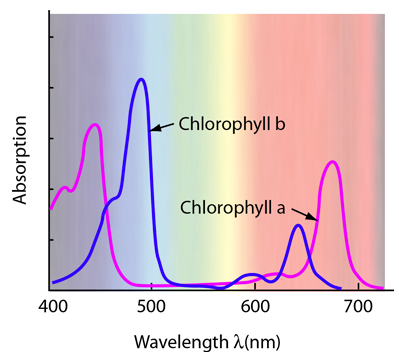
Light Absorption for Photosynthesis

Action spectrum - Wikipedia
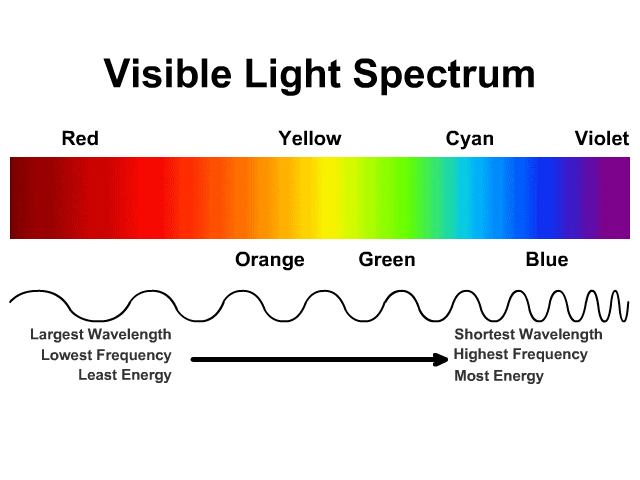
Color of Light - StickMan Physics