Dye - Synthetic, Organic, Colorants
Dye - Synthetic, Organic, Colorants: Perkin’s accidental discovery of mauve as a product of dichromate oxidation of impure aniline motivated chemists to examine oxidations of aniline with an array of reagents. Sometime between 1858 and 1859, French chemist François-Emmanuel Verguin found that reaction of aniline with stannic chloride gave a fuchsia, or rose-coloured, dye, which he named fuchsine. It was the first of the triphenylmethane dyes and triggered the second phase of the synthetic dye industry. Other reagents were found to give better yields, leading to vigorous patent activity and several legal disputes. Inadvertent addition of excess aniline in a fuchsine preparation resulted in the
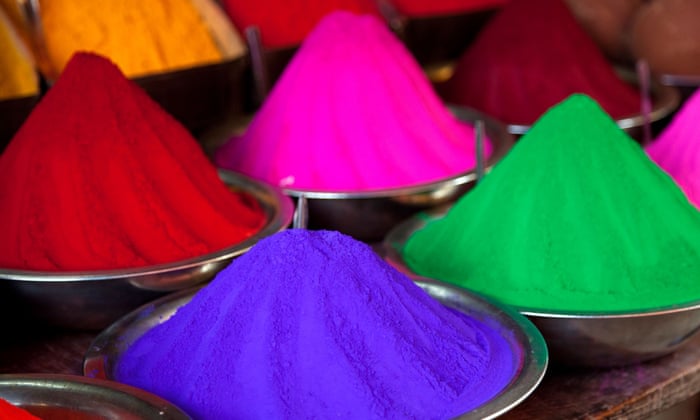
Dye, substance used to impart color to textiles, paper, leather, and other materials such that the coloring is not readily altered by washing, heat, light, or other factors to which the material is likely to be exposed. Learn more about the properties, uses, and development of dyes in this article.

Pigment - Wikipedia
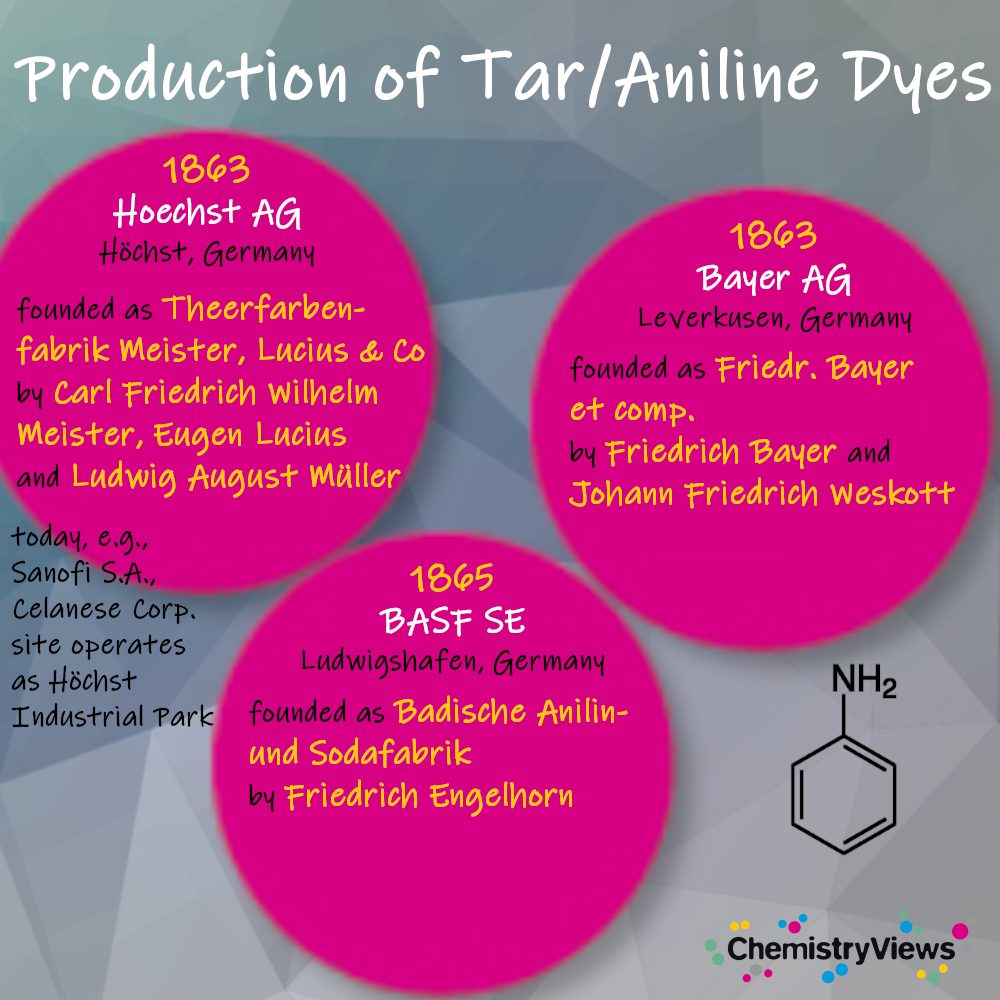
History of Synthetic Dyes - ChemistryViews

Dye - Synthetic, Organic, Colorants
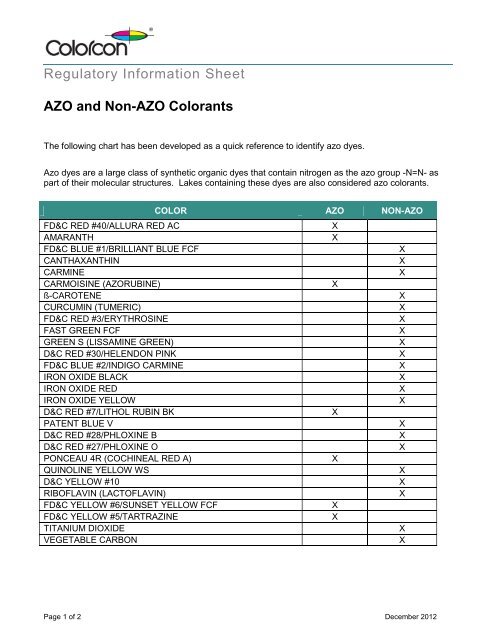
AZO and Non-AZO Colorants - Colorcon

Dye - Wikipedia
Organic Pigments

Observing Organic Dye Chemical Clock Reactions

Synthetic Dye And Pigment Market Growth Rate, Statistics, Trends By 2032

Chemical and Synthetic Dyes

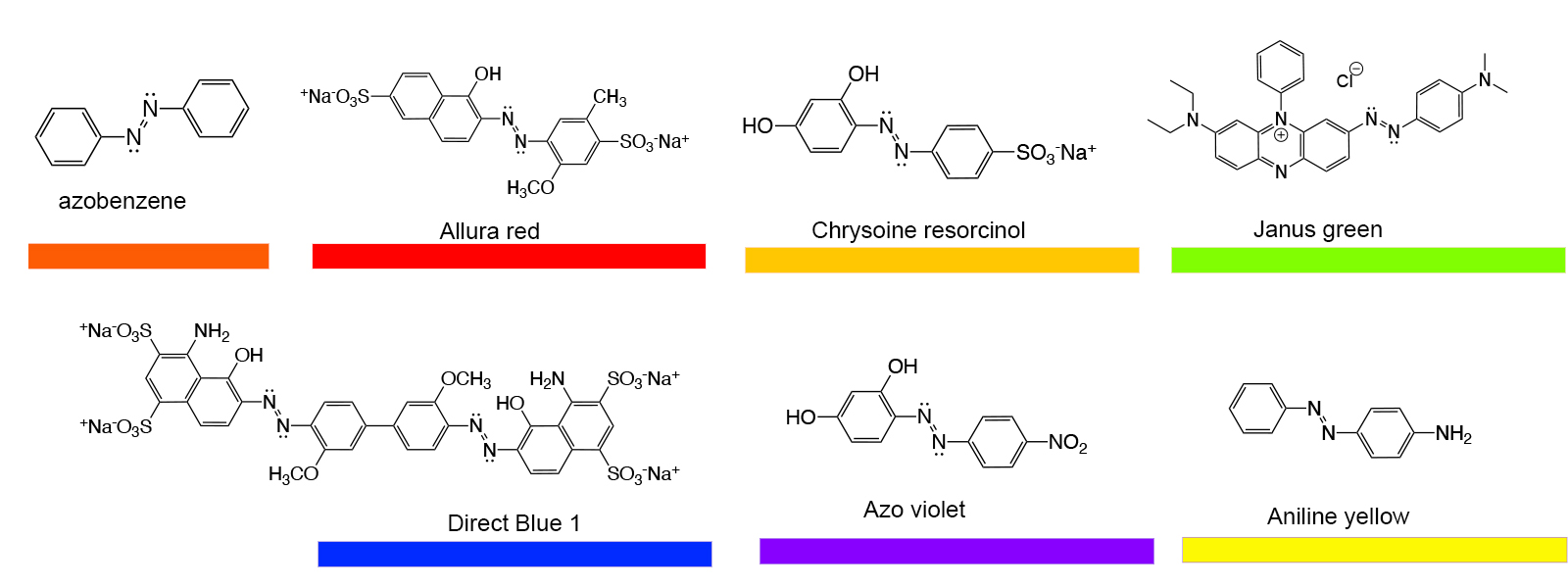
Chemical structures of synthetic dyes.

Do or dye: Synthetic colors in wastewater pose a threat to food chains worldwide

Pigments, Business & Products

What is Pigments and What are the Types of Pigments?
Aline Dye's Instagram, Twitter & Facebook on IDCrawl









