4: Fatty acids. (A) Stearic acid (saturated). (B) Elaidic acid
Download scientific diagram | 4: Fatty acids. (A) Stearic acid (saturated). (B) Elaidic acid (unsaturated, trans). (C) Oleic acid (unsaturated, cis). from publication: Modeling of biomembranes: from computational toxicology to simulations of neurodegenerative diseases | It was known from the middle of the last century that a cell-membrane is a lipid bilayer. Since that time a large number of experimental studies has been done in order to see how a certain molecule can penetrate through a membrane. Due to the complexity of laboratory | Lipid Bilayer, Biomembranes and Membranes | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.

Stearic Acid Derivative - an overview

Stearic Acid - an overview
4: Fatty acids. (A) Stearic acid (saturated). (B) Elaidic acid
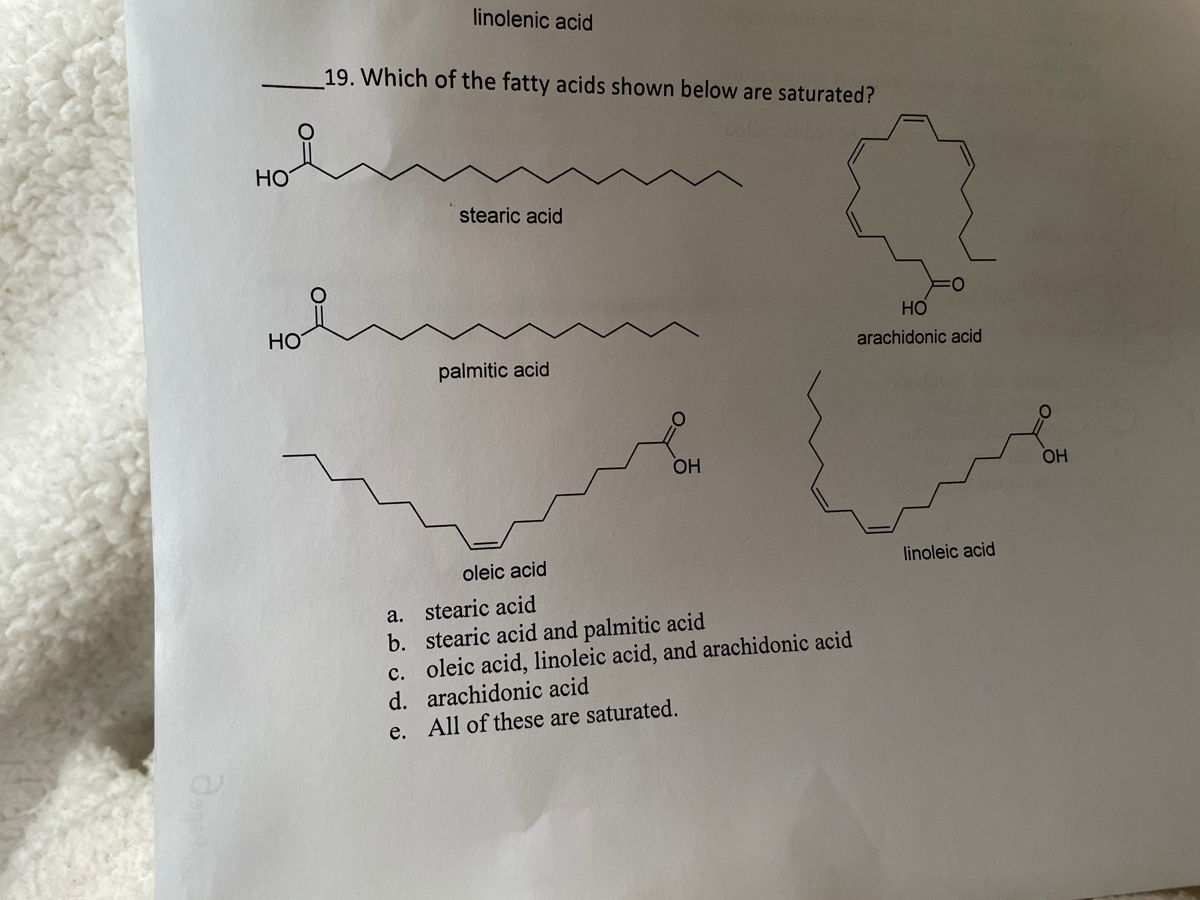
Answered: 19. Which of the fatty acids shown…

Unveiling the Structure and Reactivity of Fatty-Acid Based (Nano)materials Thanks to Efficient and Scalable 17O and 18O-Isotopic Labeling Schemes

Structures of most common fatty acids found in phospholipids. (A)
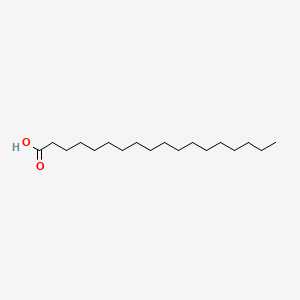
Stearic Acid, C18H36O2
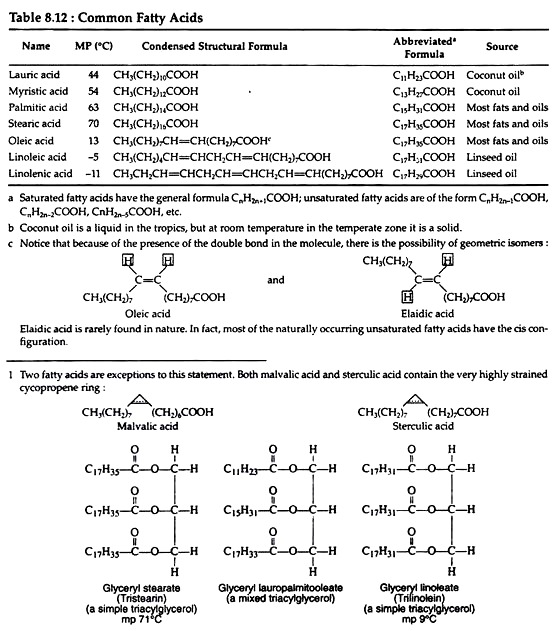
Fatty Acids: Meaning, Roles and Nomenclature
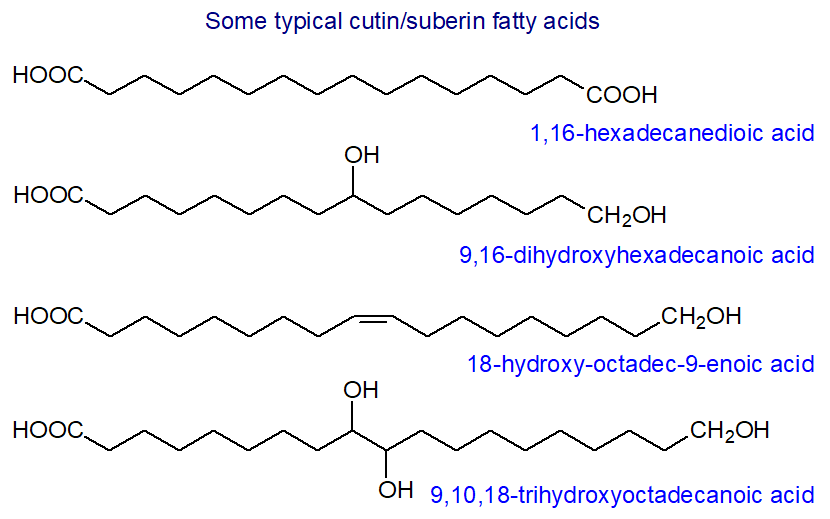
Fatty Acids: Hydroxy, furanoid, epoxy, keto and other oxygenated - composition and biochemistry
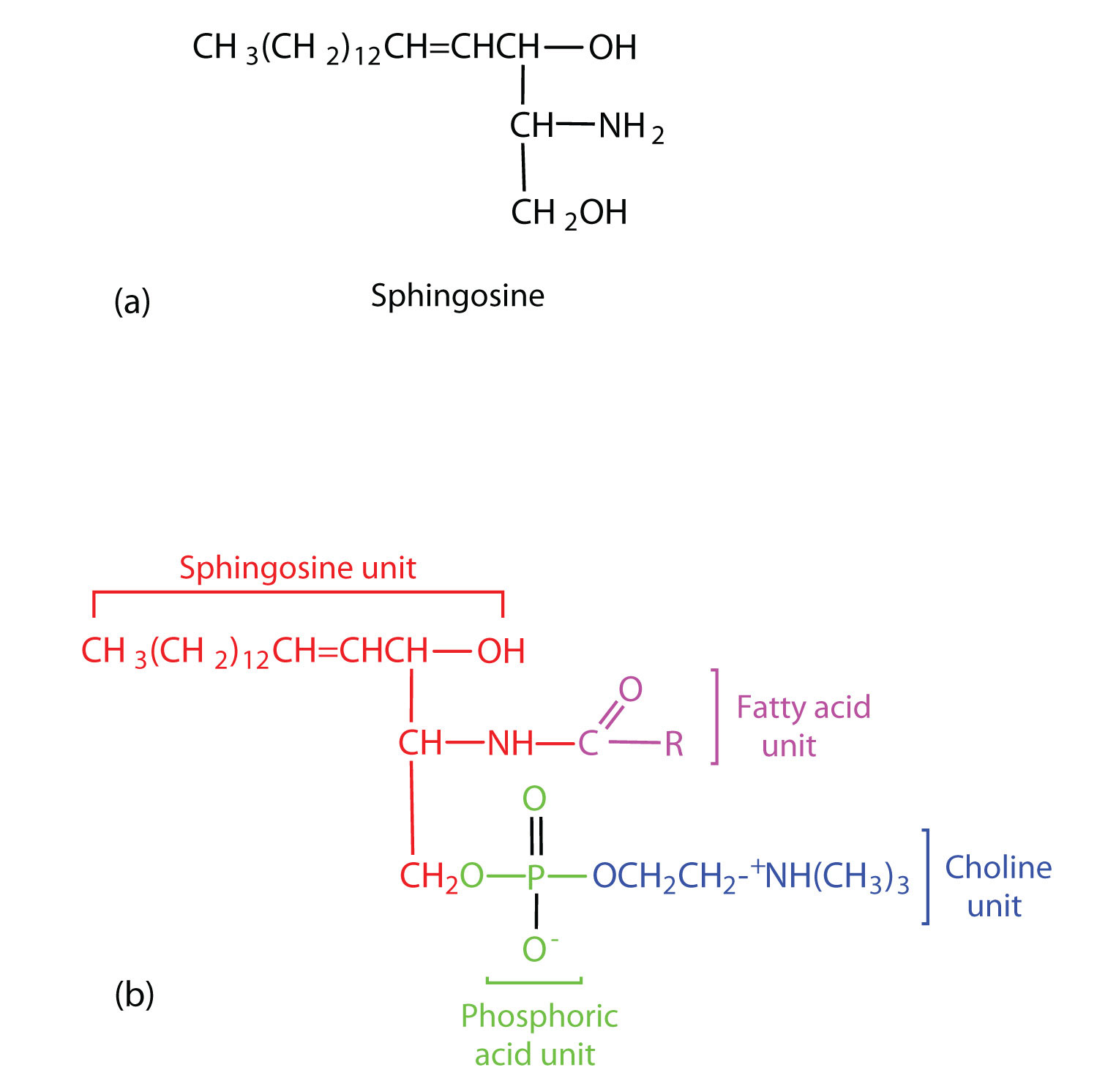
Chapter 7 - Lipids - CHE 120 - Introduction to Organic Chemistry - Textbook - LibGuides at Hostos Community College Library

Figure 1 from Influence of Trans Fatty Acids on Health









