Review of the Evidence from Epidemiology, Toxicology, and Lung Bioavailability on the Carcinogenicity of Inhaled Iron Oxide Particulates

Full article: Endogenous doesn't always mean innocuous: a scoping review of iron toxicity by inhalation
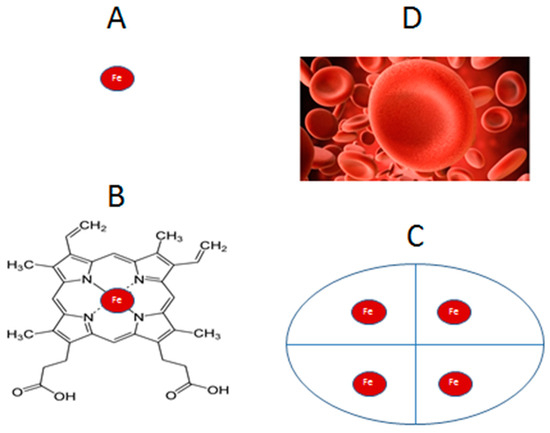
IJMS, Free Full-Text

A suspected bronchial carcinoma

Review of the Evidence from Epidemiology, Toxicology, and Lung Bioavailability on the Carcinogenicity of Inhaled Iron Oxide Particulates

Review of the Evidence from Epidemiology, Toxicology, and Lung Bioavailability on the Carcinogenicity of Inhaled Iron Oxide Particulates

Insights into the toxicity of iron oxides nanoparticles in land snails - ScienceDirect

Review of the Evidence from Epidemiology, Toxicology, and Lung Bioavailability on the Carcinogenicity of Inhaled Iron Oxide Particulates

Bioaccessibility, bioavailability and toxicity of commercially relevant iron- and chromium-based particles: in vitro studies with an inhalation perspective, Particle and Fibre Toxicology

Studying and Assessing the Toxicity of Calcium Oxide Nanoparticles under One-Time Inhalation Exposure

PDF) Actin plays a crucial role in the phagocytosis and biological response to respirable quartz particles in macrophages

PDF) Potential Toxicity and Underlying Mechanisms Associated with Pulmonary Exposure to Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Conflicting Literature and Unclear Risk

A critical review of approaches and limitations of inhalation bioavailability and bioaccessibility of metal(loid)s from ambient particulate matter or dust - ScienceDirect

Manganese and iron transport across pulmonary epithelium American Journal of Physiology-Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology


.jpg)