Optimization of a NOx and VOC Cooperative Control Strategy Based on Clean Air Benefits

Sensitivities of Ozone Air Pollution in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Area to Local and Upwind Precursor Emissions Using Adjoint Modeling
Flow of observable response indicator development and application.

The co-benefits of clean air and low-carbon policies on heavy metal emission reductions from coal-fired power plants in china - ScienceDirect

The co-benefits of clean air and low-carbon policies on heavy metal emission reductions from coal-fired power plants in china - ScienceDirect

An acid rain–friendly NH3 control strategy to maximize benefits toward human health and nitrogen deposition - ScienceDirect
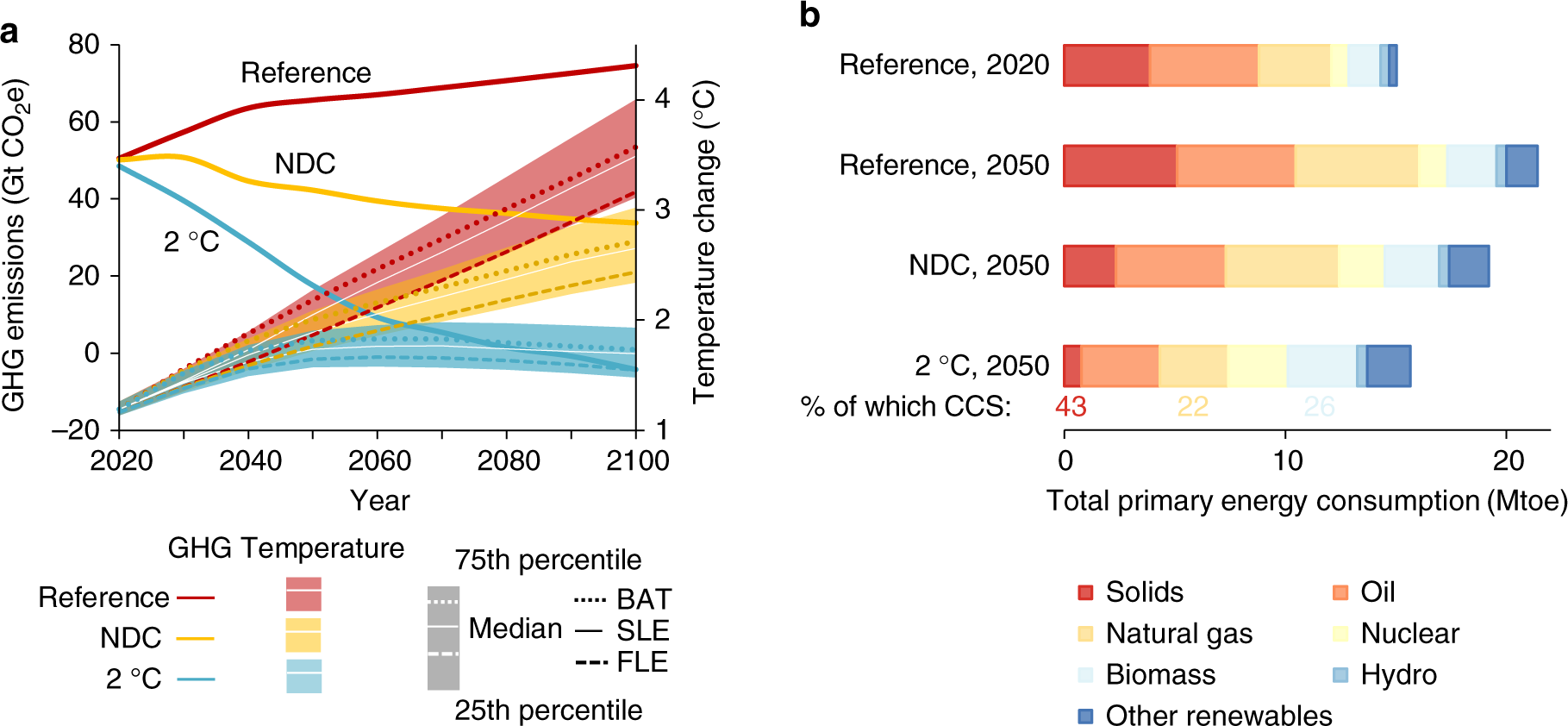
Air quality co-benefits for human health and agriculture counterbalance costs to meet Paris Agreement pledges

The RIR values for anthropogenic NMHCs from different PMF-resolved

Impacts of aerosol direct effects on PM2.5 and O3 respond to the reductions of different primary emissions in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei and surrounding area - ScienceDirect
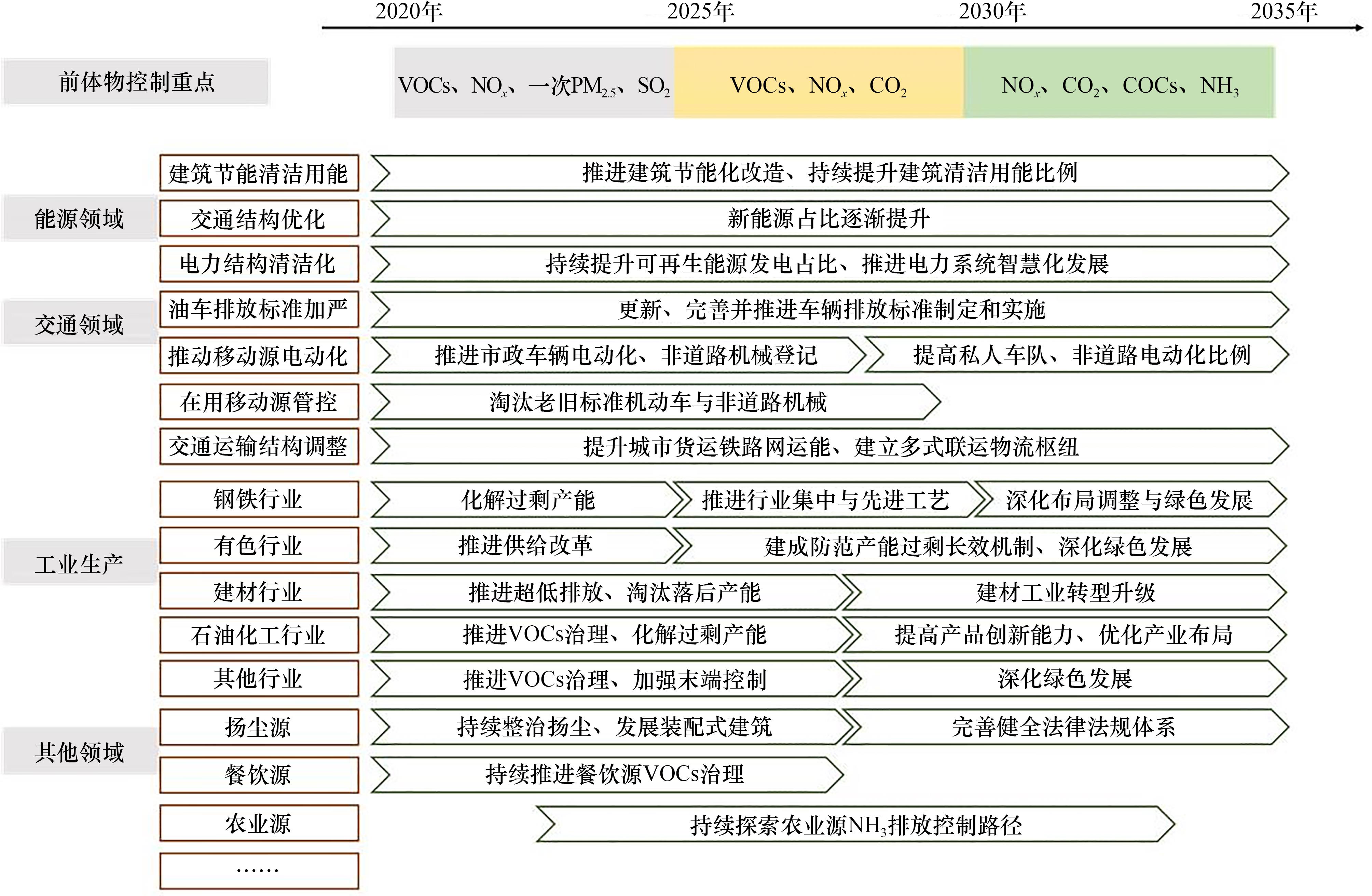
气候协同的区域空气质量精细化调控战略研究

Observations and explicit modeling of summer and autumn ozone formation in urban Beijing: Identification of key precursor species and sources - ScienceDirect

A flowchart illustrating the ERSM technique using the simplified case

11 VOC Versus NOx Controls, Rethinking the Ozone Problem in Urban and Regional Air Pollution








