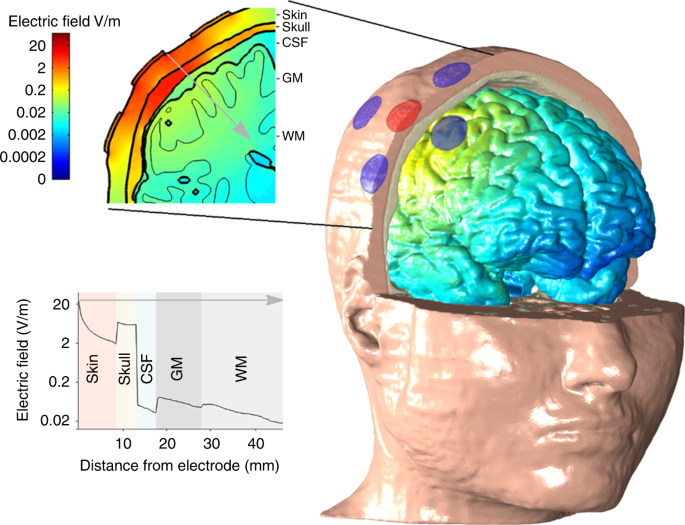
tACS motor system effects can be caused by transcutaneous stimulation of peripheral nerves
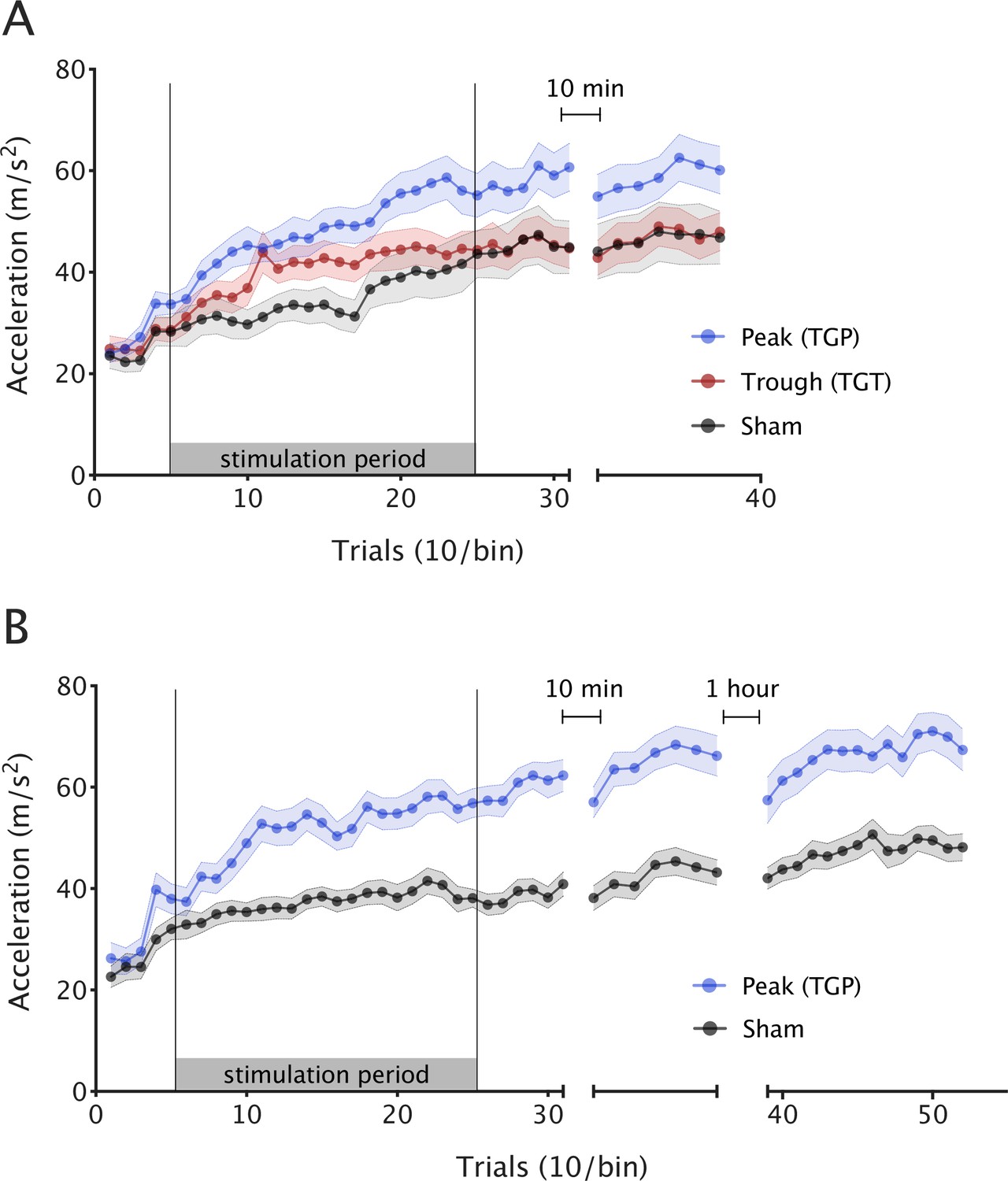
Increasing human motor skill acquisition by driving theta–gamma

In-vivo phase-dependent enhancement and suppression of brain oscillations by transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS)

Transcranial Random Noise Stimulation Acutely Lowers the Response Threshold of Human Motor Circuits
Conducting double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trials of

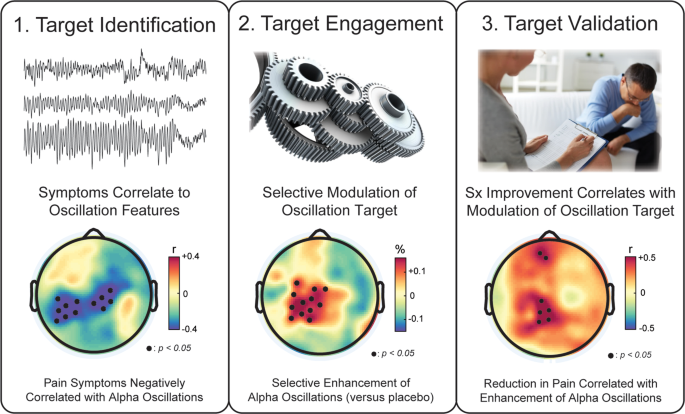
Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation to Modulate Alpha

Slow-oscillatory tACS does not modulate human motor cortical

In vivo phase-dependent enhancement and suppression of human brain oscillations by transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS) - ScienceDirect

Sensation threshold and intensity ratings. The left panel shows

PDF) tACS motor system effects can be caused by transcutaneous stimulation of peripheral nerves

PDF) Online and offline effects of transcranial alternating current stimulation of the primary motor cortex

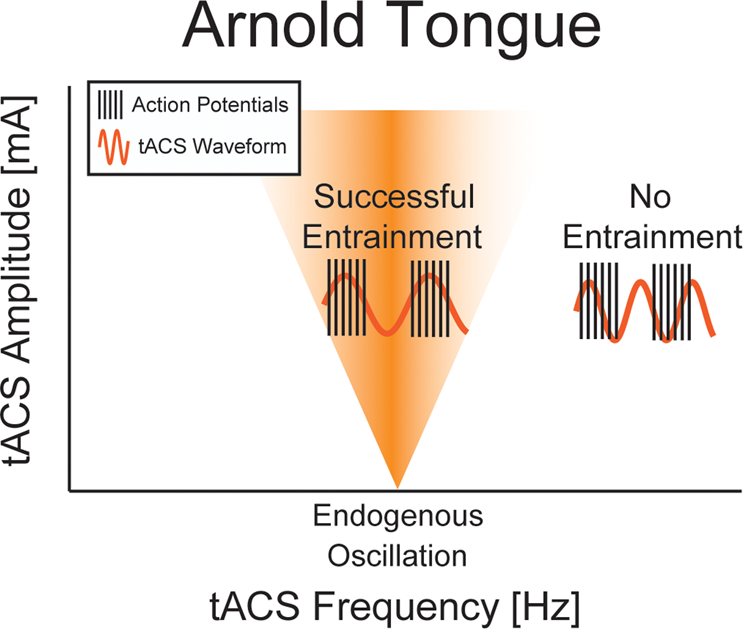
PDF] How does transcranial alternating current stimulation entrain

Transcranial alternating current stimulation entrains alpha

Standard intensities of transcranial alternating current

Potential role for peripheral nerve stimulation on learning and

Cortico–subcortical spatiotemporal dynamics in Parkinson's disease